Robert F. Bourque, Ph. D., P.E.
Bourque Engineering LLC
Los Alamos, New Mexico USA
bob@rfbourque.net
505-412-0194
Typical figures discussed in detail later:
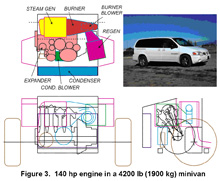
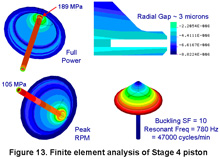
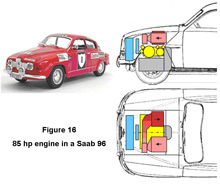
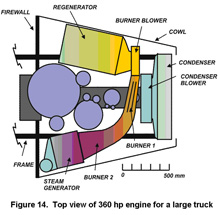
A Compact Pollution-Free
External Combustion Engine
with High Part-Load Efficiency
Brief Summary:
An external combustion engine using steam is described which has good efficiency at full power and even better efficiency at the low power settings common for passenger vehicles. The engine is compact with low weight per unit power. All of its components fit in the engine compartment of a front-wheel drive vehicle despite the space occupied by the transaxle. It readily fits in a rear-drive vehicle.
Calculated net efficiencies, after accounting for all losses, range, depending on engine size, from 28-32% at full power increasing to 33-36% at normal operating part-load power settings. The part-load efficiencies are 50-100% higher than gasoline engines and about the same as diesel engines.
Pollution-free combustion is due to a two-stage burner, 100% excess air, and combustion temperature below 1500°C. These assure complete combustion of the fuel and no nitrous oxides or carbon monoxide. The engine can cleanly burn a wide variety of fuels and fuel mixes, which should encourage the development of a diverse fuel industry. An attractive fuel blend would be methanol and ethanol with some gasoline.
Extensive software has been written that calculates full power and part-load energy balances, structural analysis and heat transfer, and performance in specified vehicles including using SAE driving cycles. Engines have been sized from 22 kW to 2400 kW. Due to this analysis, a prototype, when built, should perform as expected.
The purpose of this web site is to find someone with the passion for an engine like this and the resources needed to build that prototype. My Ph.D. is in mechanical engineering and I am a licensed Professional Engineer for the State of New Mexico. Therefore this is a serious engineering effort. The engine is not based on century-old steam engine folklore, but on modern mechanical engineering principles using sophisticated software that includes thermodynamics, compact heat exchanger design, and finite-element structural analysis.
(Note: There are numerous links to references interspersed throught this document, enclosed in brackets "[ ]". If you click these links to view the associated reference, you need to press the "Back" button on your browser to return to where you came from.)
